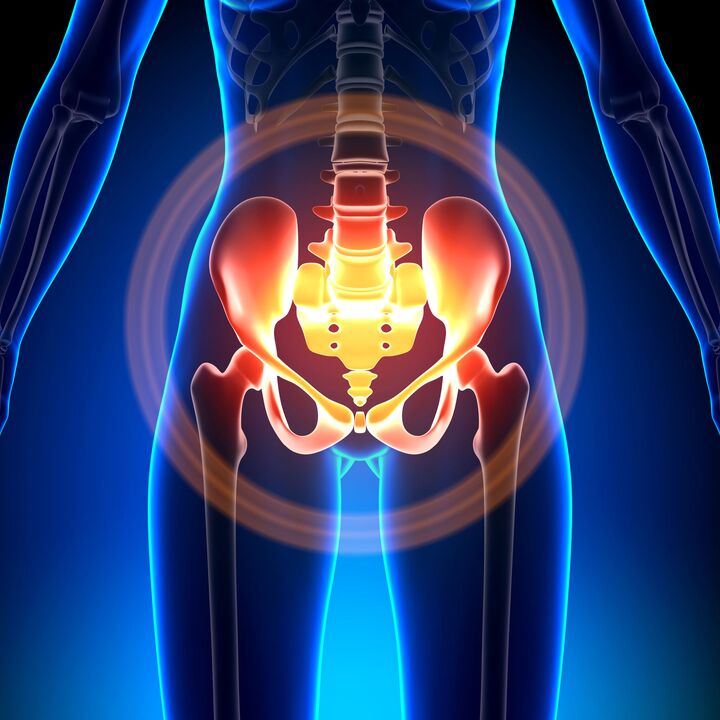
In women, varicose veins of the small pelvis (ectasia, parametrium, dilatation, or phlebostasis) are caused by this condition due to the reverse flow of blood in the ovarian artery, which occurs due to compression of the blood vessels.
Intensification of disease development is pregnancy.
The internal varicose veins of the small pelvis are expressed by strong and prolonged pain in the lower abdomen.
In the literature, varicose veins of the small pelvis are also referred to by the terms "pelvic venous edema syndrome", "varicocele in women", "chronic pelvic pain syndrome".
In the vast majority of cases (80%), varicose transformation affects the ovarian veins and is very rare (1%) in the wide ligament veins of the uterus.
According to modern medical approaches, treatment of VVMT should be carried out not so much in terms of gynecology, but primarily in terms of phlebology.
Reasons for the appearance of pathology
Most often, pelvic vein ectasia is defined in women. Moreover, usually in gynecology this disease is diagnosed in patients aged 20-40 years.
Often, patients with varicose veins of the small pelvis first try treatment at home. Folk methods used without the advice and recommendation of a doctor can cause adverse side effects, so after a certain period of time you should consult a phlebologist.
The main factors that lead to the detection of this pathology include:
- Excessively increased physical activity.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Congenital diseases of the walls of blood vessels - weakening, plasticity, underdevelopment.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Hormonal imbalance.
Pathology of sexual plan - anorgasmia, pain and the appearance of discomfort during sexual intercourse, which have a psychological etiology of appearance, while very often they have interrupted sexual intercourse.
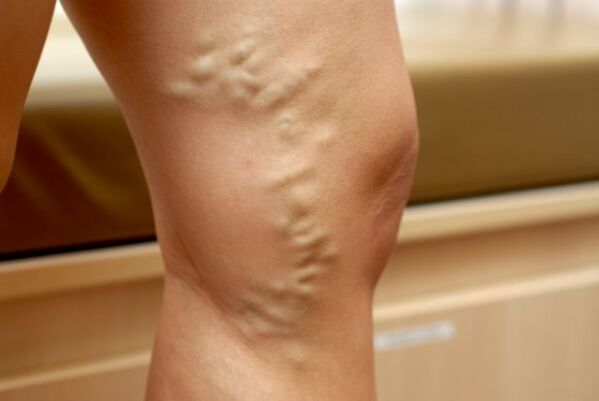
At the same time, varicose veins of the small pelvis, the treatment and symptoms of this disease are similar to varicose veins in the legs. In this situation, the venous valves begin to disrupt the work of the valves, which stimulate blood circulation to the heart muscle.
Dysfunction of the valves occurs, which act as a protection against reverse blood flow.
If their work is disrupted, then blood stagnation in the veins begins. Blood-filled veins increase in volume, which further increases the phenomenon of stagnation.
Pelvic venous edema usually occurs in the vulva, fallopian tubes, around the uterus, and possibly even dilated veins in the vagina.
The first signs and symptoms
A number of major clinical symptoms indicate the development of varicose veins. The most important of the signs of this disease is unexplained pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, often they begin to radiate to the perineum or lumbar region. The patient is also irritated by the abundant discharge of mucus from the vagina, especially in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
In addition to the main symptoms, there are other very important symptoms of varicose veins:
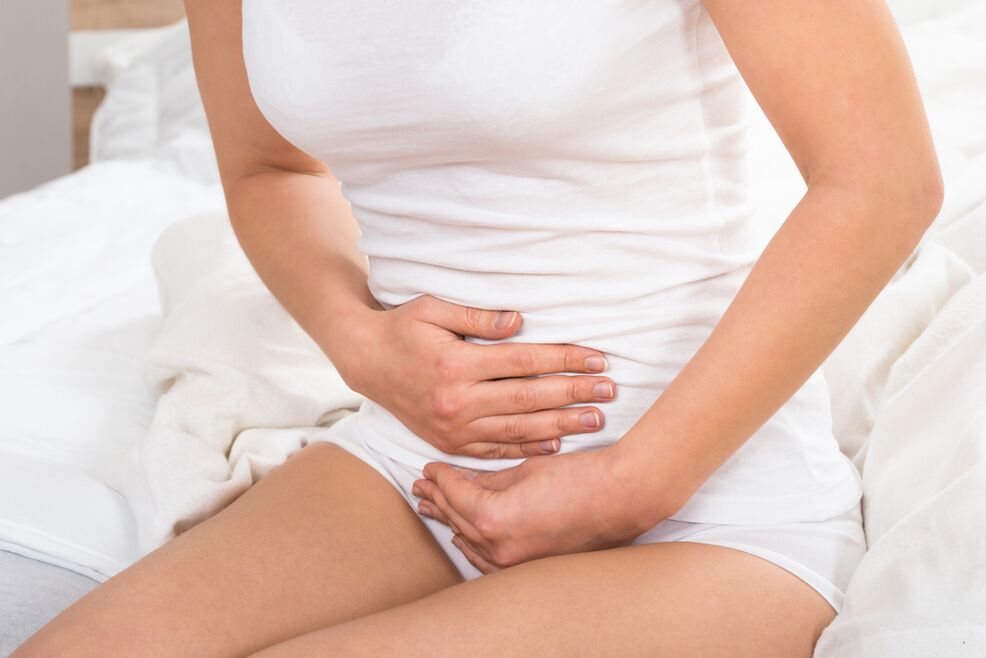

- In some cases, infertility is observed in women.
- Dysmenorrhea. Manifestation of pain during menstruation.
- Observable passage of premenstrual symptoms.
- Irradiation of pain in the groin, waist and sacrum.
- Symptom of dyspareunia (manifestation of discomfort in the vagina or vulva, both during sexual intercourse and after its completion).
- Manifestation of painful crisis (as a result of severe hypothermia of the body, excessive physical fatigue, psycho-emotional stress).
- Appearance of pain in the abdomen after prolonged overload (dynamic or static).
Before this clinical symptomatology it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, because this pathology can have a large number of unpleasant complications:
- Varicose veins can be a contraindication to natural childbirth;
- The work of the reproductive organs is violated;
- There is a fear of sexual contact;
- Irritability and anxiety arise.
It should also be noted that all of the above symptoms can manifest in different ways, with all signs of the disease observed in individual patients, and in some only a few of them.
Methods of diagnosing the disease
To make a correct diagnosis, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination. If a woman complains of pain that arises for an unknown reason, then the specialist first of all identifies all the causes that are the factors in the manifestation of the pain symptom. The patient's lower limbs are carefully examined. So you can detect the manifestation of varicose veins. In some situations, the diagnosis is made by a vascular doctor.
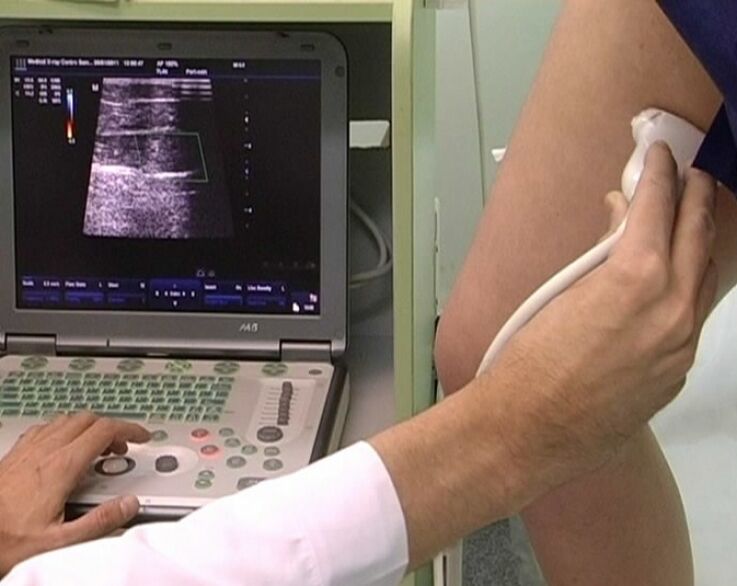
The main diagnostic methods are as follows:
- Venous system ultrasound. The examination makes it possible to examine the tortoiseshell and varicose veins.
- Laparoscopy. Identify varicose veins in the ovarian region.
- CT. This makes it possible to rule out disease, identify varicose veins in the ovaries and uterus, see magnification on the monitor, and also see their inclination.
- Selective ovulation. The most accurate examination. It is performed by injecting a contrast substance into the subclavian and femoral veins.
- Doppler ultrasonography. Determines the reduction of the systolic rate of the process in the veins of the ovaries and uterus.
The use of these methods allows to more clearly define the symptoms of the disease.
Degrees and differential approach
To standardize the possibility of approach to diagnosis and differential treatment, A. E. Volkov divided varicose veins according to the site of venous ectasia and the size of the dilated vessels.
There are three stages of this disease:
- The first stage - the movement of the "cover" of the vessel, the size of the vein is not more than 6 mm;
- Second stage - the size of the vein is not more than 7-11 mm in the general type of varicose veins, VR of the uterine arc vein, parametric vein VR, loose ectasia of the ovary;
- Stage 3 - The size of the vein is more than 11 mm during the basic form of parametric formation or the whole type of VR.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, you can use healing or surgical methods.
Methods of treatment of varicose veins
Conservative methods of therapy (corrective gymnastics, NPS drugs, venotonics) are most often used in stages 1-2 of varicose veins.

Conservative therapy in venous edema syndrome is symptomatic, which includes the normalization of rest and physical activity, which excludes excessive active load and prolonged standing.
When a patient is diagnosed with varicose veins, the treatment procedures are primarily aimed at achieving the following tasks:
- Relieve bleeding symptoms, pain, etc. Sh.
- Restore venous tone, increase blood circulation in tissues.
- Interruption of reverse blood flow through the venous system of the ovaries.
It is important to realize that even very high quality therapy for this pathology cannot cure varicose veins.
However, adequate treatment will make it possible to prevent major clinical symptoms and significantly improve the patient's condition.
EMCT treatment includes several key components:
- Regular exercise in medical gymnastics to prevent disease.
- Course of drug use during exacerbation.
Conservative therapy of affected veins
Due to the internal location of the veins infected with the pathology, the medications are used orally, making it simply impossible to apply venous ointments and gels.
The following drugs are used for this disease:
- Horse chestnut extract - to relieve inflammation and swelling.
- Diosmin-based - to remove high elasticity of blood vessels, to prevent damage, to reduce permeability.
- Vitamin C - strengthens blood vessel walls.
Doctors recommend combining conservative treatment with exercise therapy as well as the use of compression underwear. Compression garments are especially needed during pregnancy.
surgery
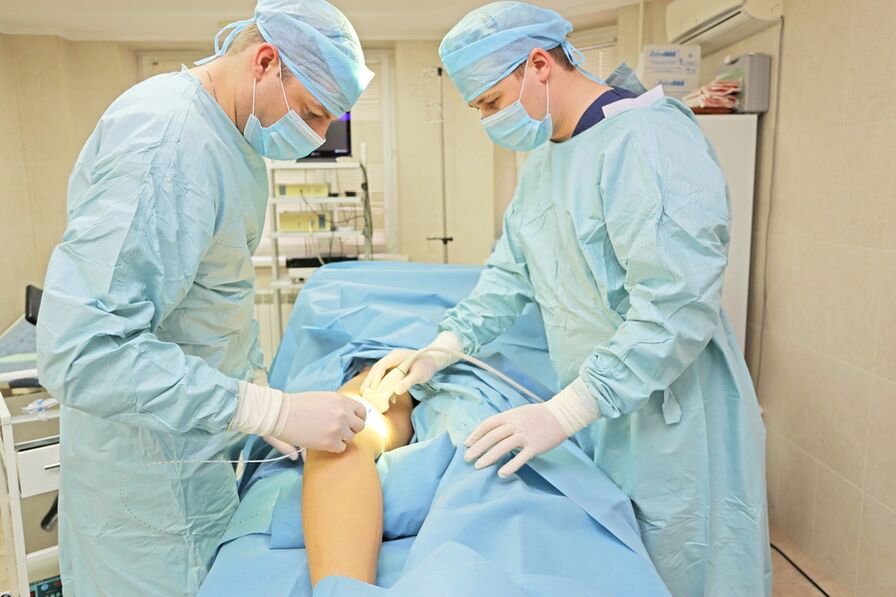
Surgical intervention is an extreme method of treatment used if the disease is at a very advanced stage and there is an assumption of venous VR.
The surgery is selected based on the location of the major venous rupture and includes the following interventions:
- Surgery crocectomy - also used in diseases of the veins of the legs;
- Venous ligation in the genitals (usually done in parallel with perineal miniflectomy);
- Ligation of the ovarian vein.
If surgery is necessary, the choice of appropriate manipulations is quite individual, since everything will depend on the location of the varicose veins.
In exercise and corrective gymnastics
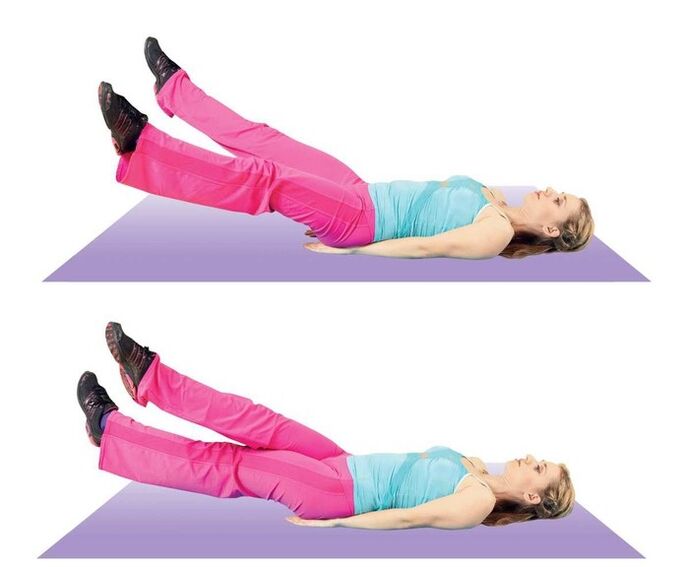

If we take into account the necessary physical exercises, then women with this disease need at least one exercise every day - "vodka", "bicycle", "scissors".
Also very helpful is a contrast shower in the pelvis and breathing exercises. At the same time, proper and effective gymnastics is the fastest way to restore a healthy and normal life.
The simplest but most effective exercises are:
- Raise your legs while lying on your back, then bend over and lift as high as possible. The exercise is done about 10 times.
- In a supine position, stretch your legs, then bend, reaching to your chest. Move at least 10 times.
- You will have to walk around the room for half an hour. First - on the toes, then - on the heels, then - raise the knees as high as possible.
- Lie on your stomach, take turns lifting your legs up. In the maximum position, the leg should be fixed for a few seconds. At least 7 approaches for each foot.
Folk recipes and remedies
Varicose veins can be treated at home.
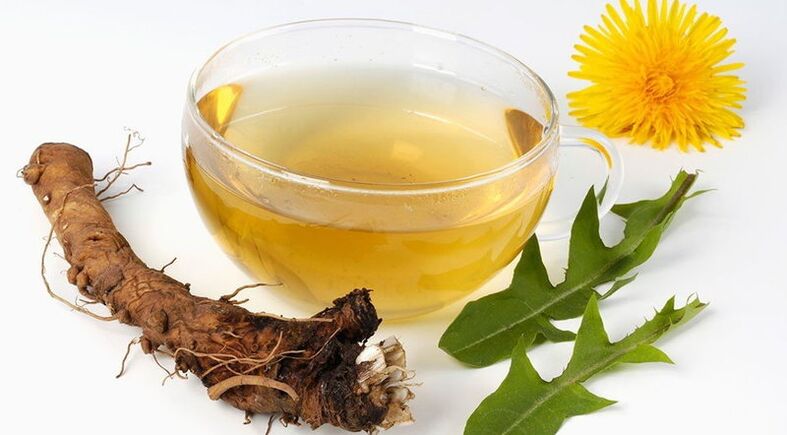

The most famous and common folk methods of treatment:
- Horse chestnut infusion.
- Kombucha tincture.
- Dandelion root tincture.
- Treatment with fleas used in the area of Kudusuni and Sasi.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of varicose veins. The daily diet should be balanced and contain enough fiber and natural proteins.
Preventive actions
It is also important to use a few simple tips to help prevent VVMT. Moreover, if they are constantly monitored, they can also improve the overall condition of the body:
- Exercise every day.
- Use special tights for treatment.
- Add more vegetables to your daily diet. Avoid foods that cause constipation.
- Take a break from sedentary work, walking for at least 10 minutes every two hours.
- Do not use alcohol or smoke.
- Do not take hormonal drugs uncontrollably.
- After surgery for VVMT, you should take prophylactic doses of the medication prescribed by your doctor.
Possible prognosis
If the varicose condition is not considered at all, then after a certain period the veins grow even more (by 90%), this threatens serious side effects including thrombosis. In the remaining 10% of varicose veins in which she developed after pregnancy, the disease does not progress to a more severe stage, although it never resolves on its own.
If you start treating the pathology, you can achieve complete recovery (15-25%, depending on the severity) or significant improvement (55-60%), especially in the case of a simultaneous combination of surgical and conservative methods. . But, one way or another, after prophylactic therapy, continuous prophylaxis should be carried out, which includes maintaining a proper lifestyle, regular medication or supporting venous contraction.




































